Satellite
Nothing is Motionless, The universe is constantly moving
A satellite is a body that moves around another body that is under study, like the Earth. Some satellites are man-made while others are natural. The artificial satellites are placed in space to revolve and serve a specific purpose. The force of gravity makes the object relevant to the researcher. Though humans has sent thousands of satellites to space, it is observed that close to three-quarters of them have ceased being functional.. Planets that orbit other stars are referred to as Exoplanets.
Nevertheless, humans has been able to better understand the universe and other planets, as well as the moon. This has enabled us to advance in all sectors. Satellites can be grouped into natural and artificial.
Explore in Silence

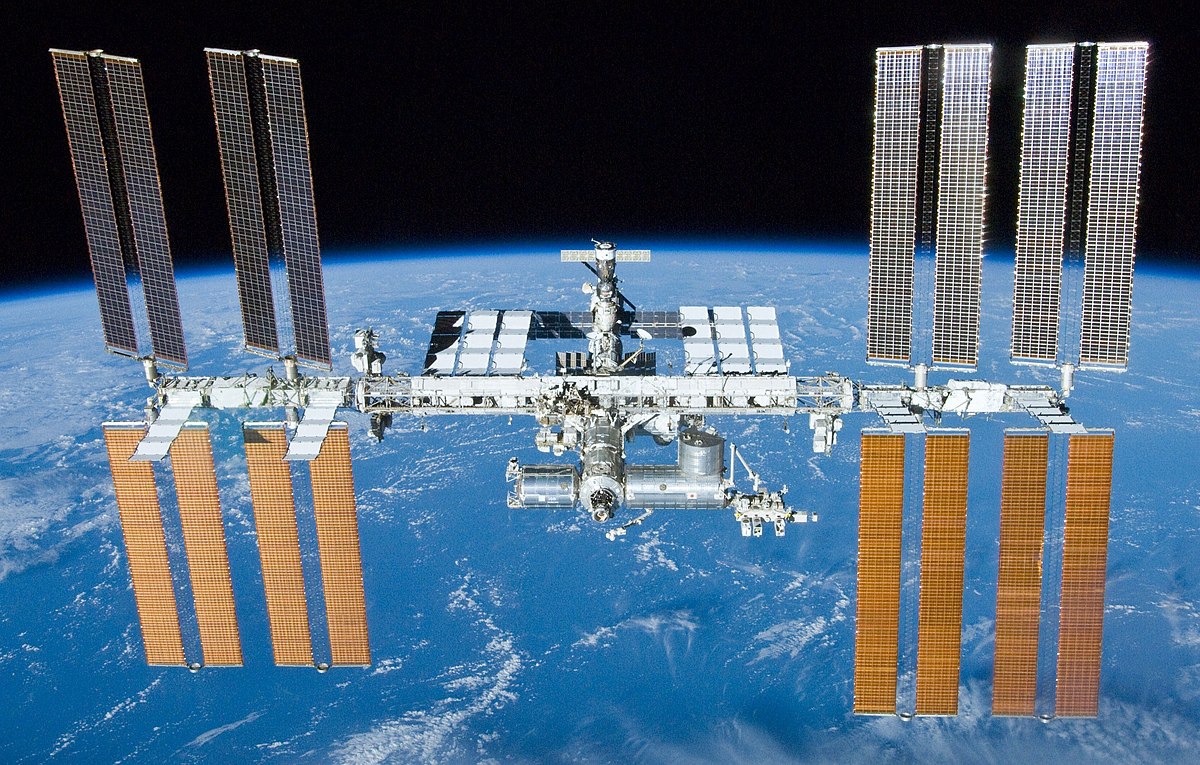 INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION(ISS)
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION(ISS) The International Space Station (ISS) is a multi-nation construction project that is the largest single structure humans ever put into space. Its main construction was completed between 1998 and 2011, although the station continually evolves to include new missions and experiments. It has been continuously occupied since Nov. 2, 2000. As of January 2018, 230 individuals from 18 countries have visited the International Space Station. Top participating countries include the United States (145 people) and Russia (46 people).
Astronaut time and research time on the space station is allocated to space agencies according to how much money or resources (such as modules or robotics) that they contribute. The ISS includes contributions from 15 nations. NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia) and the European Space Agency are the major partners of the space station who contribute most of the funding; the other partners are the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
Current plans call for the space station to be operated through at least 2024, with the partners discussing a possible extension until 2028. Afterwards, plans for the space station are not clearly laid out. It could be deorbited, or recycled for future space stations in orbit.
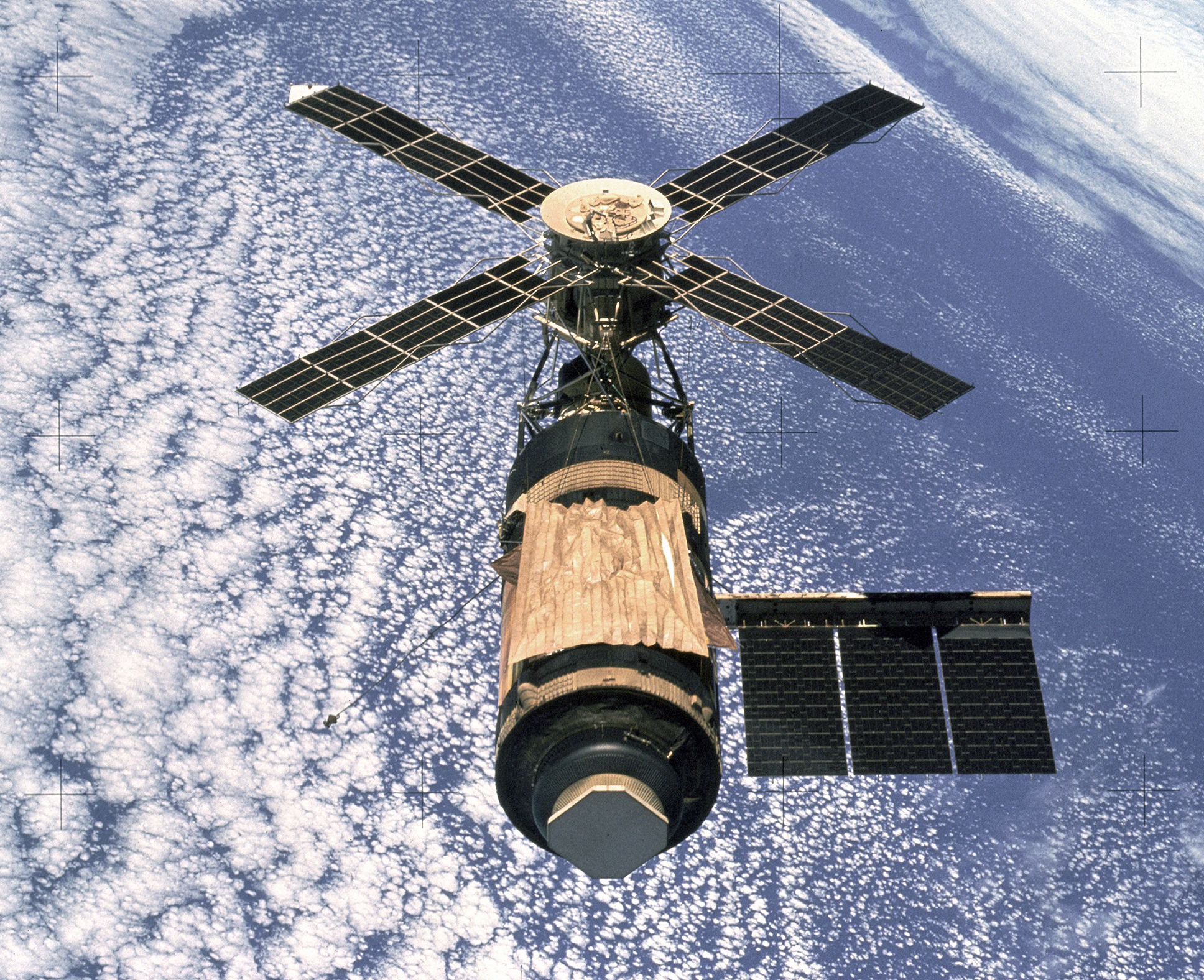 Skylab
Skylab Skylab was America’s first space station and first crewed research laboratory in space. Early visions of orbiting space stations predated the Space Age and the Soviet Union orbited its first experimental space station Salyut in 1971.!
 Sputnik
Sputnik The Sputnik 1 spacecraft was the first artificial satellite successfully placed in orbit around the Earth and was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome at Tyuratam (370 km southwest of the small town of Baikonur) in Kazakhstan, then part of the former Soviet Union.
The Russian word "Sputnik" means "companion" ("satellite" in the astronomical sense).
 Starlink
Starlink Starlink is a satellite internet constellation being constructed by SpaceX providing satellite Internet access.
The constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), working in combination with ground transceivers.
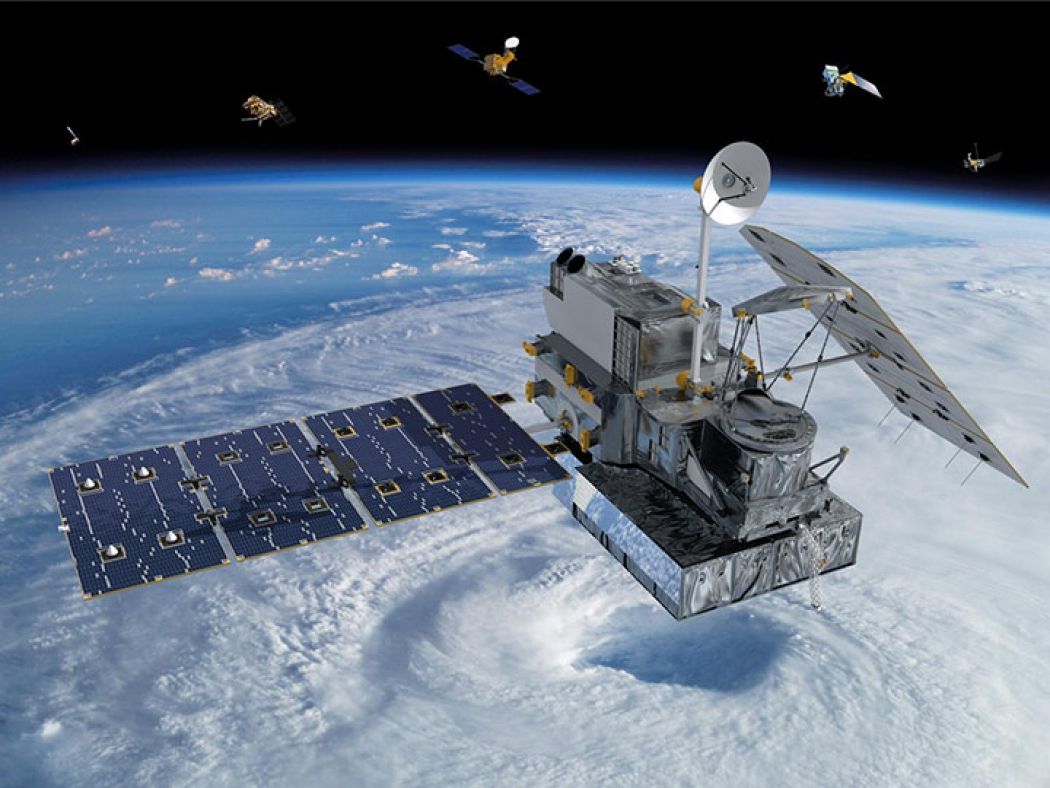 Weather Satellite
Weather Satellite The weather satellite is a type of satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting, covering the entire Earth asynchronously, or geostationary, hovering over the same spot on the equator.
Meteorological satellites see more than clouds: city lights, fires, effects of pollution, auroras, sand and dust storms, snow cover, ice mapping,
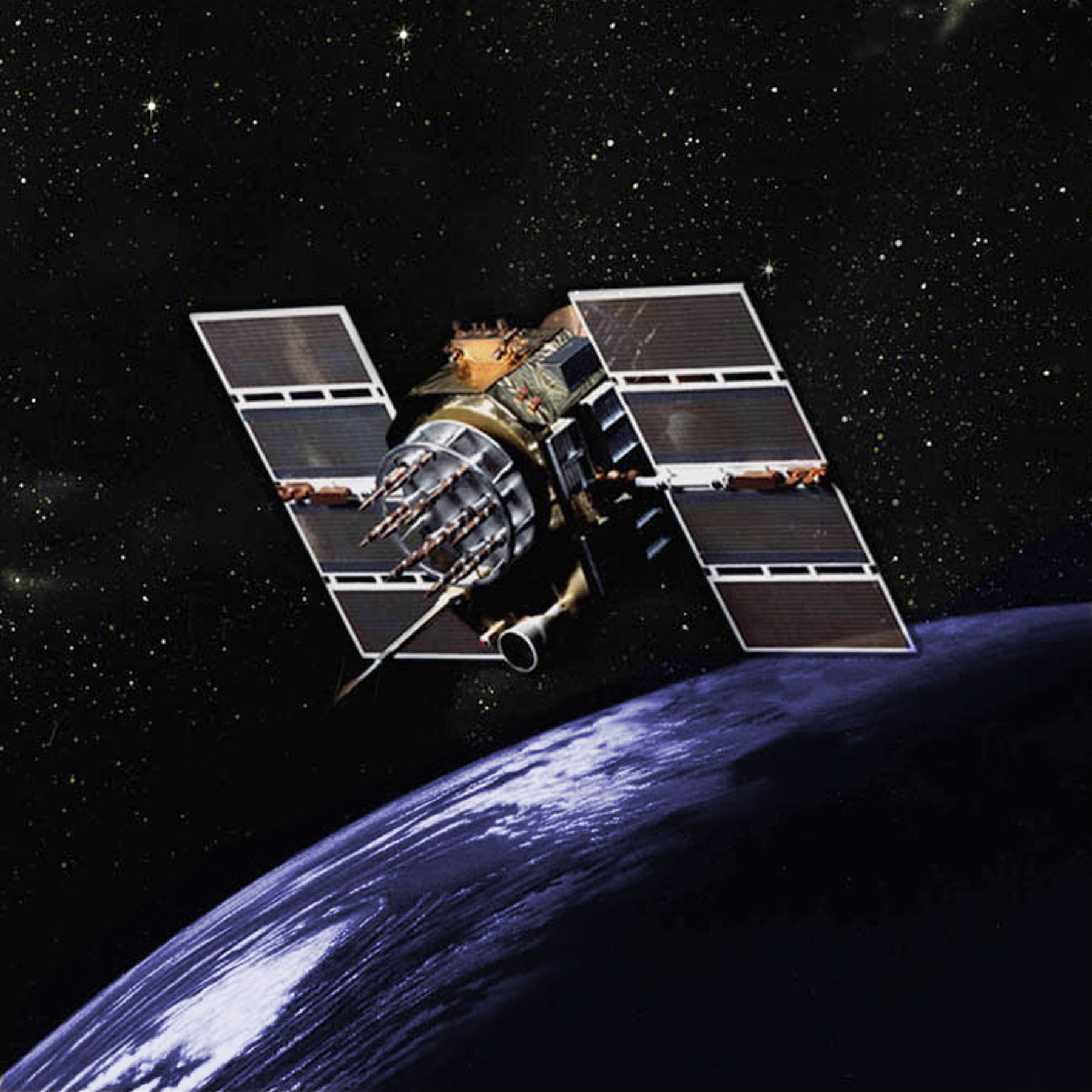 The Global Positioning System (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS (stylized in capital letters in its logo), is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth.
 Earth Observation Satellite
Earth Observation Satellite An Earth observation satellite or Earth remote sensing satellite is a satellite used or designed for Earth observation (EO) from orbit, including spy satellites and similar ones intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, cartography and others.
The most common type are Earth imaging satellites, that take satellite images, analogous to aerial photographs;
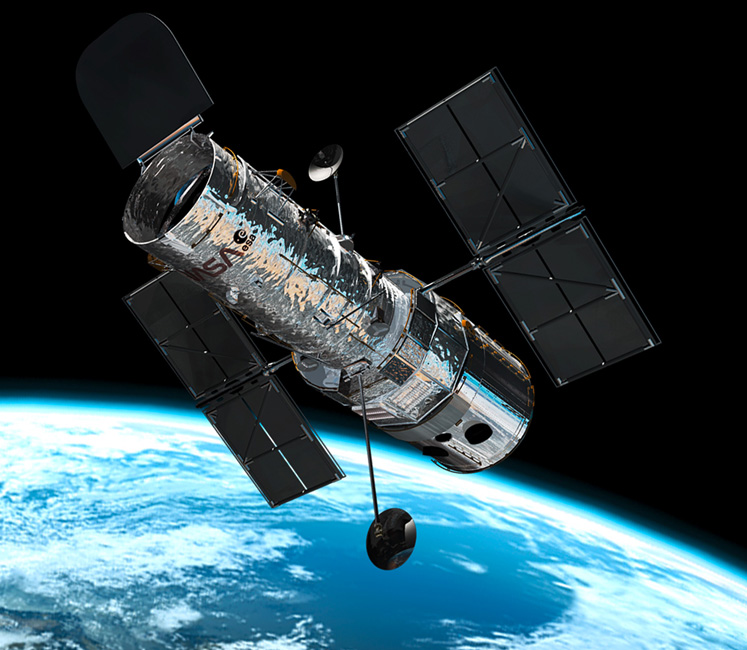 Astronomical Satellite
Astronomical Satellite
An astronomy satellite is basically a really big telescope floating in space. Because it is in orbit above the Earth, the satellite's vision is not clouded by the gases that make up the Earth's atmosphere, and its infrared imaging equipment is not confused by the heat of the Earth.
Astronomy satellites, therefore, can "see" into space up to ten times better than a telescope of similar strength on Earth.

 Astronaut
Astronaut