Rockets
A Technology Propelling Humanity to Discover the Unknown Universe
Rocket, any of a type of jet-propulsion device carrying either solid or liquid propellants that provide both the fuel and oxidizer required for combustion. The term is commonly applied to any of various vehicles, including firework skyrockets, guided missiles, and launch vehicles used in spaceflight, driven by any propulsive device that is independent of the atmosphere..
The rocket differs from the turbojet and other “air-breathing” engines in that all of the exhaust jet consists of the gaseous combustion products of “propellants” carried on board. Like the turbojet engine, the rocket develops thrust by the rearward ejection of mass at very high velocity.
The fundamental physical principle involved in rocket propulsion was formulated by Sir Isaac Newton.
According to his third law of motion, the rocket experiences an increase in momentum proportional to the momentum carried away in the exhaust,
 What is Thrust
What is Thrust All rockets are propelled by engines that produces thrust. The force produced by burning fuel, as the gas escape through the engine of the rocket.Thrust is the force which moves an aircraft through the air. Thrust is used to overcome the drag of an airplane, and to overcome the weight of a rocket. Thrust is generated by the engines of the aircraft through some kind of propulsion system.
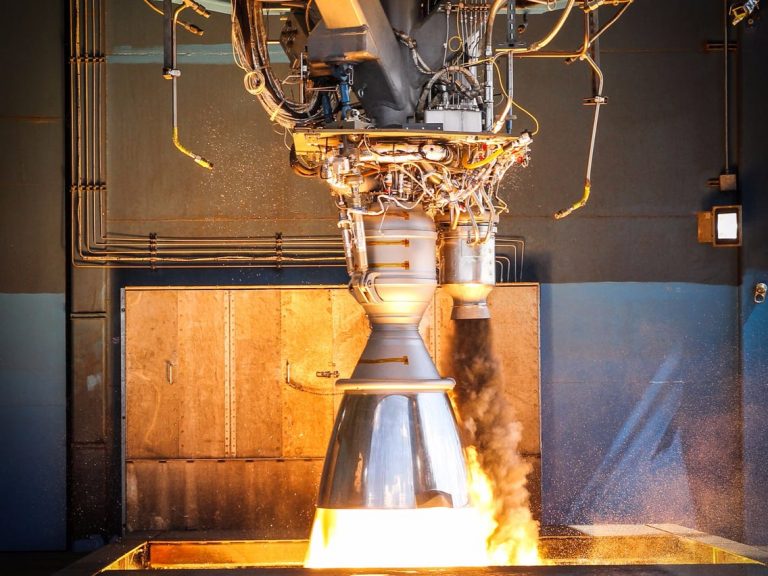 Rocket Engine
Rocket Engine Rocket engines are reaction engines. The basic principle driving a rocket engine is the famous Newtonian principle that "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction." A rocket engine is throwing mass in one direction and benefiting from the reaction that occurs in the other direction as a result. When most people think about motors or engines, they think about rotation. For example, a reciprocating gasoline engine in a car produces rotational energy to drive the wheels. An electric motor produces rotational energy to drive a fan or spin a disk. A steam engine is used to do the same thing, as is a steam turbine and most gas turbines. Rocket engines are fundamentally different.
Rocket engines are reaction engines. The basic principle driving a rocket engine is the famous Newtonian principle that "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction." A rocket engine is throwing mass in one direction and benefiting from the reaction that occurs in the other direction as a result.
 Cylindrical System
Cylindrical System The structural system of a rocket is like an outer skeleton which includes all of the parts which make up the frame of the rocket, i.e. the cylindrical body, the control fins, and the fairings. The function of the structural system is to minimize the amount of aerodynamic drag created during the flight.
The cylindrical rocket shell has a second advantage in that it acts as a pressure vessel to contain the pressurised propellants. The internal pressure of the propellants increases the circumference of the rocket shell, and like blowing up a balloon, imparts tensile stretching deformations into the skin which preempt the compressive gravitational and inertial loads.
 Nose System
Nose System The aerodynamic shape of the nose cone helps prevent air from slowing the rocket.
The nose cone is usually the part that first interacts with the air in flight. The nose cone parts the air as the rocket moves through the atmosphere. Pushing the air out of the rocket’s way creates friction. The friction pushes the nose cone downward, transferring the air’s force to the airframe. The rocket’s passage through the air creates heat of friction; for most model rockets, this heat is trivial, because it lasts only for a few seconds. However, for a slender high-powered rocket that flies several miles high at twice the speed of sound.
 Fins System
Fins System The fins help the rocket keep pointing in the direction it launched. When a rocket is flying through the air, changes in the air can make the rocket wobble. If it wobbles too much it can go off course.
Having the right size, shape, and amount of fins will help make sure your rocket corrects itself when it wobbles.
 Propulsion System
Propulsion System The propulsion of a rocket includes all of the parts which make up the rocket engine; the tanks pumps, propellants, power head, and rocket nozzle.
The function of the propulsion system is to produce thrust. Thrust is the force which moves a rocket through the air and through space. Thrust is generated by the propulsion system of the rocket.
 Rocket Fuel
Rocket Fuel Fuel Rocket engines and boosters carry both fuel and an oxidizer. For solid fuel, the components are aluminum and ammonium perchlorate. For liquid fuel, the components are liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. When combined, the fuels release water, which allows the rocket to leave the ground.
 Oxidizer
Oxidizer -Oxidizer In chemical rockets, unburned fuel or oxidizer represents the loss of chemical potential energy, which reduces the specific
 Payload System
Payload System
The payload system of a rocket depends on the rocket’s mission. (The payload system definitely will differ depending on the type of mission). Some of them are vehicles, some are experiments; some are intended to eject from the rocket. The equipment carried by a rocket, satellite, or spacecraft.
the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile , the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; the total weight of these systems is referred to as the throw-weight .
 RADARS
RADARS
A radar is tracking a rocket. At some instant of time, the distance, r, and angle, θ, are measured as 10 mi and 30º, respectively.From sucessive measurements,
the derivatives, r',r'',theta' and theta'' are estimated to be ft/s, ft/s, rad/s and rad/s, respectively. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the rocket.
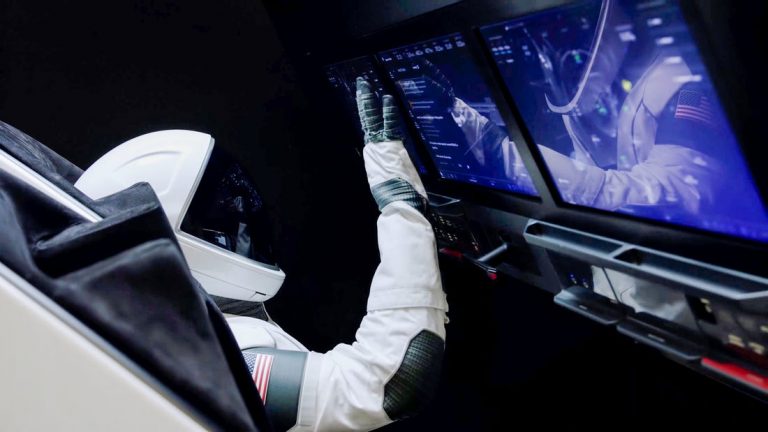 COMPUTER CONTROL
COMPUTER CONTROL
The guidance system of a rocket includes very sophisticated sensors, on-board computers, radars, and communication equipment. The guidance system has two main roles during the launch of a rocket; to provide stability for the rocket, and to control the rocket during maneuvers. Many different methods have been developed to control rockets in flight.
 ALL THESE FOUR SYSTEM MUST COME TOGETHER TO OVERCOME THE FORCE OF GRAVITY.
ALL THESE FOUR SYSTEM MUST COME TOGETHER TO OVERCOME THE FORCE OF GRAVITY.
@S - Rocket


 Rocket Lab
Rocket Lab